What is Financial Leverage?
In order to fund their growth, businesses widely use Financial Leverage. In this article, we will explain what leverage is and how you can use it to your advantage.

What is Financial Leverage?
Leverage is an investment strategy of using borrowed money to increase the potential return of an investment. To put it simply, it is the use of debt to achieve a business or finance goal.
Leverage is widely used in business, investing, and even personal finance. Families can use leverage (in the form of mortgages) to buy houses while companies and investors use leverage to boost purchasing power to buy assets and increase returns on equity capital invested.
A company, property, or investment that is said to be “highly leveraged”, means that it has significantly more debt than equity. Yet if the leverage leads to a higher investment return, compared to the rate of interest a company is paying on a loan, the level of leverage is reduced as the asset value increases.
Why use financial leverage?
In physics, leverage can help you lift heavier objects than you normally can handle. Likewise in finance, financial leverage enables you to buy more than you can normally afford.
For many businesses, borrowing money can be more advantageous than raising further equity capital or selling assets to finance transactions. This is more true especially for startups and small businesses with low capital and few assets. By taking loans or credit lines, you can finance business operations and jump-start your company until you start earning profit.
In addition to this, firms use leverage to avoid diluting shares. The use of debt (by issuing bonds and loans) instead of issuing stock (shares) to finance business operations help you keep ownership of your company and increase shareholder value.
When to use financial leverage?
As a rule of thumb, it is better to borrow when the cost of debt is relatively cheap. That is to say, when interest rates are low. This means that your monthly interest payments are typically lower than they are in periods of high interest rates.
What to remember
- Financial leverage is just another word for debt
- Leverage is used to boost investing strategies and returns
- Companies use leverage to finance their assets
- It multiplies investor’s buying power in the stock market
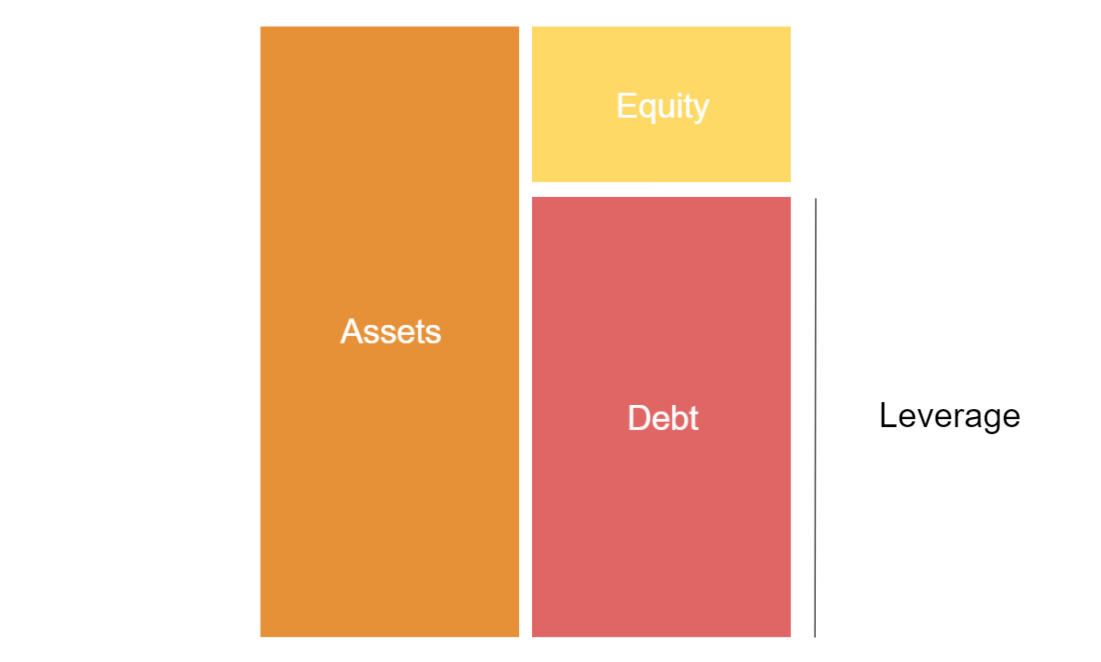
How it works
More specifically, leverage is the use of borrowed capital to pursue any project or investment. The result is a calculation of future project returns. Simultaneously, debt would also increase the potential loss if the investment does not yield higher revenue or asset value.
Taking on debt, as a company or individual, will always bring a heightened level of risk due to the fact the amount of debt must be paid back regardless of earnings or cash flows. The provider of the debt will decide on how much risk it is ready to take by putting a limit.
- In the case of asset-backed lending, the financial provider uses the assets as collateral until the borrower repays the loan.
- In the case of a cash flow loan, the general creditworthiness of the company is used to back the loan.
Effects of financial leverage
Let’s use an example. Let’s assume Company X wants to acquire a property that costs $100,000 to expand its business operations. The company can either use equity or debt to finance the investment.
Without leverage
Let’s say the company only uses equity to purchase the asset. It will own 100% of the asset and no interest payment is required. If the asset appreciates in value by 30%, the asset’s value will increase to $130,000 and the company will earn a profit of $30,000 with a return on equity of 30 (30,000/100,000). Similarly, if the asset depreciates by 30%, the asset will be valued at $70,000 and the company will incur a loss of $30,000 and have a return on equity of -30% (-30,000/100,000).
With leverage
In this case, we assume the company uses 40% equity and 60% debt.
This example involves 2.5 to 1 leverage because the investment is 2.5 times more than the amount of equity the company has.
If the asset appreciates by 30%, the asset will be valued at $130,000. It means that after the company pays back the debt of $60,000, it will have $70,000 remaining, which translates into a profit of $30,000. Given that the company has only invested $40,000 in equity and the value of the asset has gone up by $30,000, its return on equity is 75% (30,000/40,000).
Comparably, if the asset depreciates by 30%, the asset will be valued at $70,000. After paying the debt of $60,000, the company will remain with $10,000 which means a loss of $30,000 ($40,000 — $10,000). The return on equity will be -75% (-30,000/40,000).
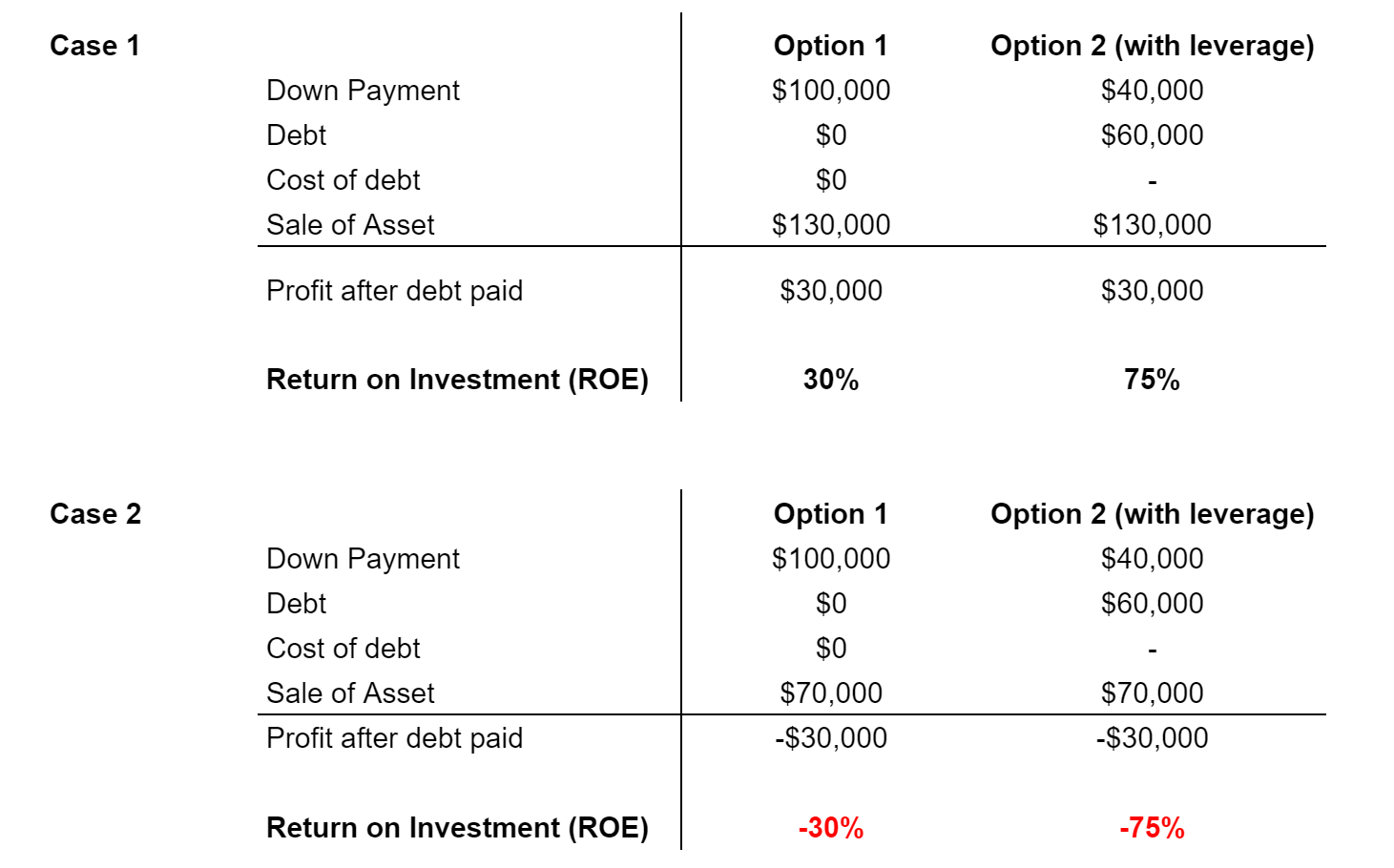
Although the profit is the same in both cases, using leverage gives a much higher return on investment because the company made $30,000 of profit with an investment of only $40,000 (instead of a $30,000 profit with a $100,000 investment).
From this example, leverage heavily impacts a company’s return on equity (ROE). The Return on Equity shows a firm’s efficiency at generating profits from every unit of shareholders’ equity.
The Risk of Leverage
Leverage can be a tricky tool. As much as it can bring more profitability to a company, it can do the opposite too. Leverage magnifies both gains and losses. If an investor uses leverage to make an investment and the investment moves against the investor, their loss is much greater than it would’ve been if they had not leveraged the investment.
Important Formulas
Return on Equity
The return on equity measures the profitability of a business in relation to its equity.
ROE = Net Income / Equity
Return on Assets
The return on assets shows the percentage of how profitable a company’s assets are in generating revenue.
ROA = Net income / Total assets
Leverage Ratio or Debt-to-Equity Ratio
This ratio is used to evaluate a company’s financial leverage by showing a company’s proportion of debt to the company’s equity.
D/E Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
A higher ratio indicates that there is more usage of creditor financing (debt) more than shareholders’ financing. For example, a leverage ratio of 2 means a company uses $2 in debt for every $1 of equity. In other words, the company’s debt level is 150% of equity.
In general, most companies do not go above a ratio of 2.0. However, the optimal debt-to-equity ratio will vary depending on the industry.
In finance, this is also known as Gearing. When there is a high proportion of debt to equity, a business is said to be highly geared.
EPS
Earnings per share (EPS) is the monetary value of earnings per outstanding share of common stock for a company.
EPS = net Income / number of shares
Conclusion
Financial leverage allows businesses to make investments that provide an alternative to issuing shares or raising equity capital. Generally, it is better to borrow money when interest rates are historically lower.
- A leveraged company is a company that takes in debt
- It is an investment strategy that helps multiply gains
- Leverage magnifies profit if the company is doing well, and can magnify losses if the company is doing poorly
- The higher the risk, the higher the reward
Here at Zetl, we help SMEs build their business by providing a variety of funding solutions. We ensure responsible leverage by only approving financing facilities that you can afford to pay back. We help you unlock working capital in less than 24 hours so you can focus on what truly matters— growing your business.
Why choose us?
We are fast and flexible. Get paid the same day after signing up. Repay at your own convenience after 30 days.
Fully digital. Complete everything online — submit documents through our web app, and all contracts are executed digitally.
Confidential. Your client never needs to know about Zetl. All financing is fully confidential.
No personal guarantees. We believe business risk should be kept separate from personal liability.
Unlock funds by signing up on our website now! — www.zetl.com