How to Prepare a Business Budget

What is budgeting?
Budgeting helps you keep track of your business’s financial health. It is a forecast of revenue and expenses over a specified period in the future. Budgets are often used by businesses, governments, and households. They are an integral part of running a business efficiently.
In this blog, we will explain why budgets are important, how to prepare a business budget and some additional tips on how to properly manage your business’s funds.
Why budgeting is important
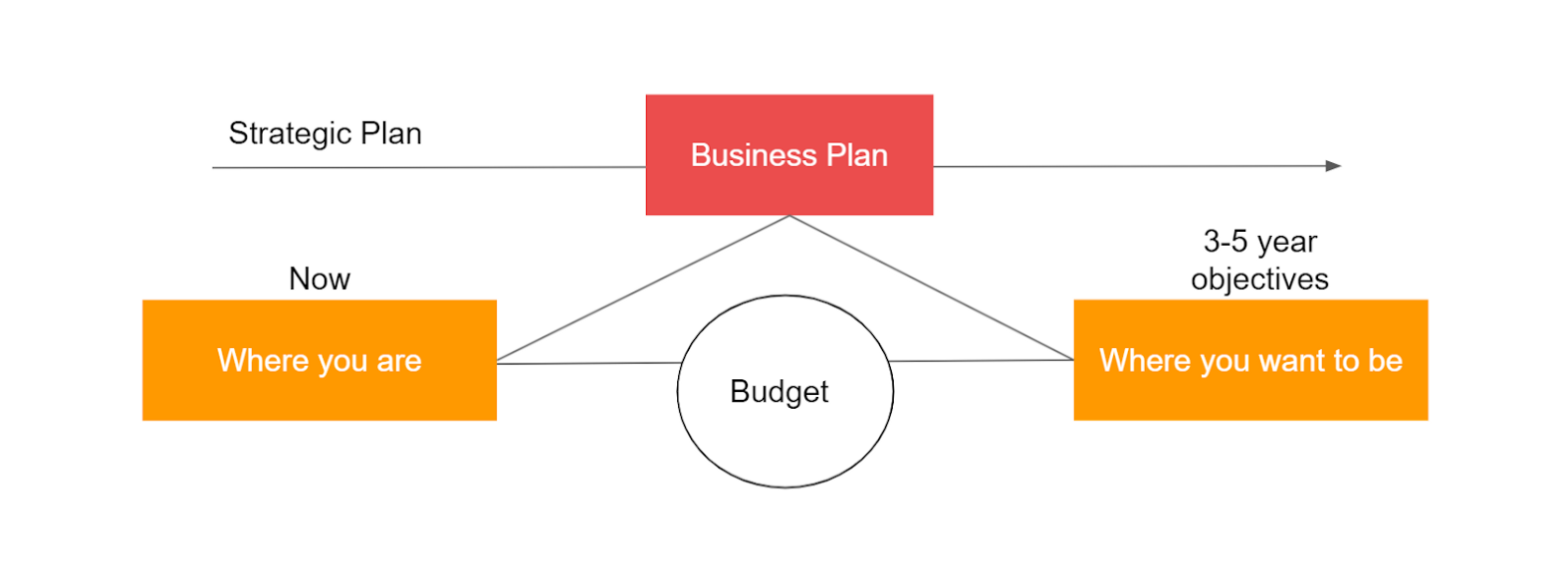
Budgeting is an important tool that helps you make informed decisions in the long run. It helps you evaluate your business’s current performance and set goals for the future. To achieve the goals in a business’s strategic plan, we need a detailed descriptive roadmap of the business plan that sets measures and indicators of performance. A budget quantifies your business goals and transforms them into targets.
A budget helps you:
- Set priorities, new goals in line with the company objectives, and spending caps
- Allocate appropriate resources to projects
- Recognize when you can hire new employees, invest in new profit lines
- Monitor performance and meet your objectives
- Make educated decisions about overhead expenses, salaries, benefits, and bonuses
- Receive credit lines*
*Most lenders require three years of cash flow statements on a month-by-month basis, and three years of quarterly and annual income statements (P&Ls). — How to create a startup budget, The Balance
How to prepare a corporate budget
Before you start, you require two essential things:
- An accounting software program or spreadsheet program
- Information on the costs associated with the sales of products
Step 1: List your essential startup cost
If you are just getting started, it is important to estimate the amount of money you’ll need to jump-start your business — meaning, the moment to open your business to the world and start receiving customers. You could call this a “day one budget” and it can be broken down into 4 main categories:
- Facilities costs — leases for a location, like a store, office, or warehouse if it isn’t a remote business
- Fixed assets — these include cars, equipment, and machinery that are essential for your business.
- Materials and supplies — office supplies, advertising, and promotion materials are examples of additional costs that will be there to support your business.
- Other costs — When starting a business, there are many one-time fees. Initial fees for your accounting system, local licenses and permits, insurance deposits, and legal fees to register your business with government entities are some examples of these costs.
Alternative Step 1: Review your Profit and Loss Statement
If you’ve been in business for a while, start by looking at your past profit and loss statements. You should look at your statements of the past two years. Average them and remove unusual expenses and one-time revenues. Adjust by taking a look at expenses that went up, modifications in gross margins, one-time investments, market conditions, and revenue during the year.
Step 2: Estimate your monthly fixed and variable costs
The next step is to determine your fixed costs, also known as overhead costs. These are expenses that largely remain the same each month and do not depend on the number of customers you have. Here are what they would look like:
- Rent or mortgage
- Payroll and benefits
- Insurance
- Website and other fixed subscriptions
- Internet, server, and phone services
- Professional services
- Bank fees
Now is a great time to evaluate your expenses. Consider taking a look at the rates you’re paying to see if you could get better rates on insurance or other services. Make sure employee compensation is in line with the company’s growth and revenue.
You should also take a look at whether you will need to hire new employees, as this will impact your capital expenditures. Having new staff on board means that you will need to spend on new computers, machinery, furniture for them to do their jobs. Equally, you might need to buy new machinery and equipment to expand or update your product.
Always remember how the investment can impact output. While it can be tempting to put off large investments, this decision can impact delivery timing, quality of product, and output, which can have a big impact on revenue over time. — How to Prepare a Corporate Budget, 2021, Indeed
Variable expenses increase or decrease depending on your sales and production, so they aren’t fixed. As you scale up, these costs generally go up, and vice versa. Here are some examples of variable expenses:
- Packaging costs
- Raw materials
- Sales commissions
- Utilities (like electricity and water)
- Shipping costs
- Credit card and bank fees
- Hourly wages and direct labor
Step 3: Estimate your Monthly sales
You will need to forecast your earnings for each type of income source. This is a tricky step of budgeting if you don’t know what sales will be for a new company. Without data from past sales, it’s best to create 3 sets of revenue projections: the most optimistic estimate of your first-year sales, the least optimistic, and the most likely scenario.
In addition to this, you should take into consideration a collection percentage. Depending on your type of business and how customers pay you, you could collect less (or more) than what you anticipate. For instance, you can set a collection percentage of 85%: if you estimate sales in month one to be $50,000, you should predict your cash for the month to be $42,500.
Step 4: Create a Cash Flow statement
Now, with the estimate of your expenses and profits, you can create a cash flow statement. Cash flow is the total amount of money being transferred into and out of a business.
Managing your cash flow is essential for keeping your business afloat. Cash flow is often said to be more important than profits. You could be making a great profit on paper, but if you do not have enough working capital, your business will have to shut down when it can’t pay its operating expenses.
Some additional tips
- Start as soon as you can. Creating an annual budget takes time. For it to be done properly, you should start early and coordinate efforts by you and your management team.
- Consult with other departments. Some departments will require a bigger budget than others and vice versa.
- Be transparent and involve your team. It will make your team feel more involved and could help you with interesting input.
- Ask yourself if the budget is realistic. We tend to project revenue too high and project expenses too low. If you aren’t sure whether your financial projections are accurate, consider increasing your expenses by 10% and reducing revenue by 25%.
- Practice, practice, and practice. You will see your forecasting accuracy improve.
Conclusion
A budget is a forecast of revenue and expenses over a specified period. It allows the business to track where it is financially, which allows for more effective long-term planning.
The budgeting process for companies can be challenging, particularly if customers don’t pay on time, or revenue and sales are patchy.
Here at Zetl, we help SMEs by providing a variety of funding solutions to help them stay on track with their budget and growth. We help you unlock working capital in less than 24 hours so you can focus on what truly matters — growing your business.
Why choose us?
We are fast and flexible. Get paid the same day after signing up. Repay at your own convenience after 30 days.
Fully digital. Complete everything online — submit documents through our web app, and all contracts are executed digitally.
Confidential. Your client never needs to know about Zetl. All financing is fully confidential.
No personal guarantees. We believe business risk should be kept separate from personal liability.
Unlock funds by signing up on our website now! — www.zetl.com